TOKYO, Nov 30, 2022 – (JCN Newswire) – Eisai Co., Ltd. and Biogen Inc. announced today that the results from Eisai’s large global Phase 3 confirmatory Clarity AD clinical study of lecanemab (development code: BAN2401), an investigational anti-amyloid beta (Abeta) protofibril antibody for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) due to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild AD (collectively known as early AD) with confirmed presence of amyloid pathology in the brain, were presented at the 2022 Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease (CTAD) conference, in San Francisco, California and virtually.
|
|
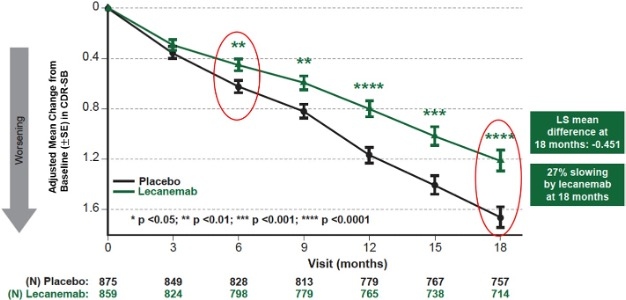
Figure 1: CDR-SB as Primary endpoint change (18 months) |
Summary of Presentations in the Scientific Session featuring Lecanemab at CTAD
Design of Clarity AD Study
Eisai’s Clarity AD was a global confirmatory Phase 3 placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, randomized study in 1,795 people with early AD (lecanemab group: 898 placebo group: 897) at 235 sites in North America, Europe, and Asia. The participants were randomized 1:1 to receive either placebo or lecanemab 10-mg/kg IV biweekly, and the randomization was stratified according to clinical subgroup (MCI due to AD or mild AD), presence or absence of concomitant approved AD symptomatic medication at baseline (e.g., acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, memantine, or both), ApoE4 status and geographical region. Eligibility criteria allowed patients with a broad range of comorbidities/comedications, including but not limited to hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, obesity, renal disease and anti-coagulants. As a result of Eisai’s recruitment strategy of diversity in the Clarity AD study, 4.5% and 22.5% of the randomized participants in the U.S. were Black and Hispanic, respectively.
The primary endpoint was change from baseline at 18 months in the CDR-SB1 (Clinical Dementia Rating Sum of Boxes), the global cognitive and functional scale, and key secondary endpoints were the change from baseline at 18 months in amyloid Positron Emission Tomography (PET) using Centiloids, AD Assessment Scale – Cognitive Subscale 14 (ADAS-Cog142), AD Composite Score (ADCOMS3) and AD Cooperative Study-Activities of Daily Living Scale for Mild Cognitive Impairment (ADCS MCI-ADL4). In addition, longitudinal changes in brain tau pathology as measured by tau PET (n=257) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers of AD pathology (n=281) were evaluated in optional sub-studies.
Efficacy Results of Clarity AD
Mean change of CDR-SB from baseline at 18 months as the primary endpoint was 1.21 and 1.66 for lecanemab and placebo groups, respectively. Lecanemab treatment resulted in highly statistically significant results, reducing clinical decline on the global cognitive and functional scale, compared with placebo at 18 months by -0.45 (95% Confidence Interval (CI): -0.67, -0.23; P=0.00005), representing a 27% slowing of decline. Starting as early as six months (difference: -0.17 [95% CI: -0.29, -0.05]; P<0.01), and increasing in absolute difference over time across all time points every 3 months, the treatment showed highly statistically significant changes in CDR-SB from baseline compared to placebo (all p-values are less than 0.01) (Figure 1).
All key secondary endpoints also showed highly statistically significant results compared with placebo (P<0.001). In the amyloid PET sub-study, treatment with lecanemab showed statistically significant reduction in amyloid plaque burden at all timepoints starting at 3 months. Mean change in Centiloids at 18 months was -55.5 and 3.6 for lecanemab and placebo groups, respectively (mean difference: -59.1 [95%CI: -62.6, -55.6]; P<0.00001). Lecanemab slowed decline of cognitive function by 26% on ADAS-Cog14 at 18 months (mean difference: -1.44 [95%CI: -2.27, -0.61]; P=0.00065). In the ADCOMS assessment, lecanemab slowed disease progression by 24% at 18 months (mean difference: -0.050 [95% CI: -0.074, -0.027; P=0.00002]). Lecanemab slowed decline of activities of daily living by 37% on ADCS MCI-ADL at 18 months (mean difference: 2.016 [95%CI: 1.208, 2.823]; P<0.00001). In addition, the primary stratified analysis showed consistent results in CDR-SB, ADAS-Cog14 and ADCS MCI-ADL at 18 months of treatment with lecanemab in all subgroups of disease stage (MCI due to AD or mild AD), ApoE4 status (non-carriers, carriers), presence or absence of concomitant approved AD symptomatic medication, and region (North America, Asia, Europe).
For more information, visit www.eisai.com/news/2022/pdf/enews202285pdf.pdf.
Source: Eisai
Copyright 2022 JCN Newswire . All rights reserved.
Featured image: © healthHFJO3